Performance
CPU benchmarks
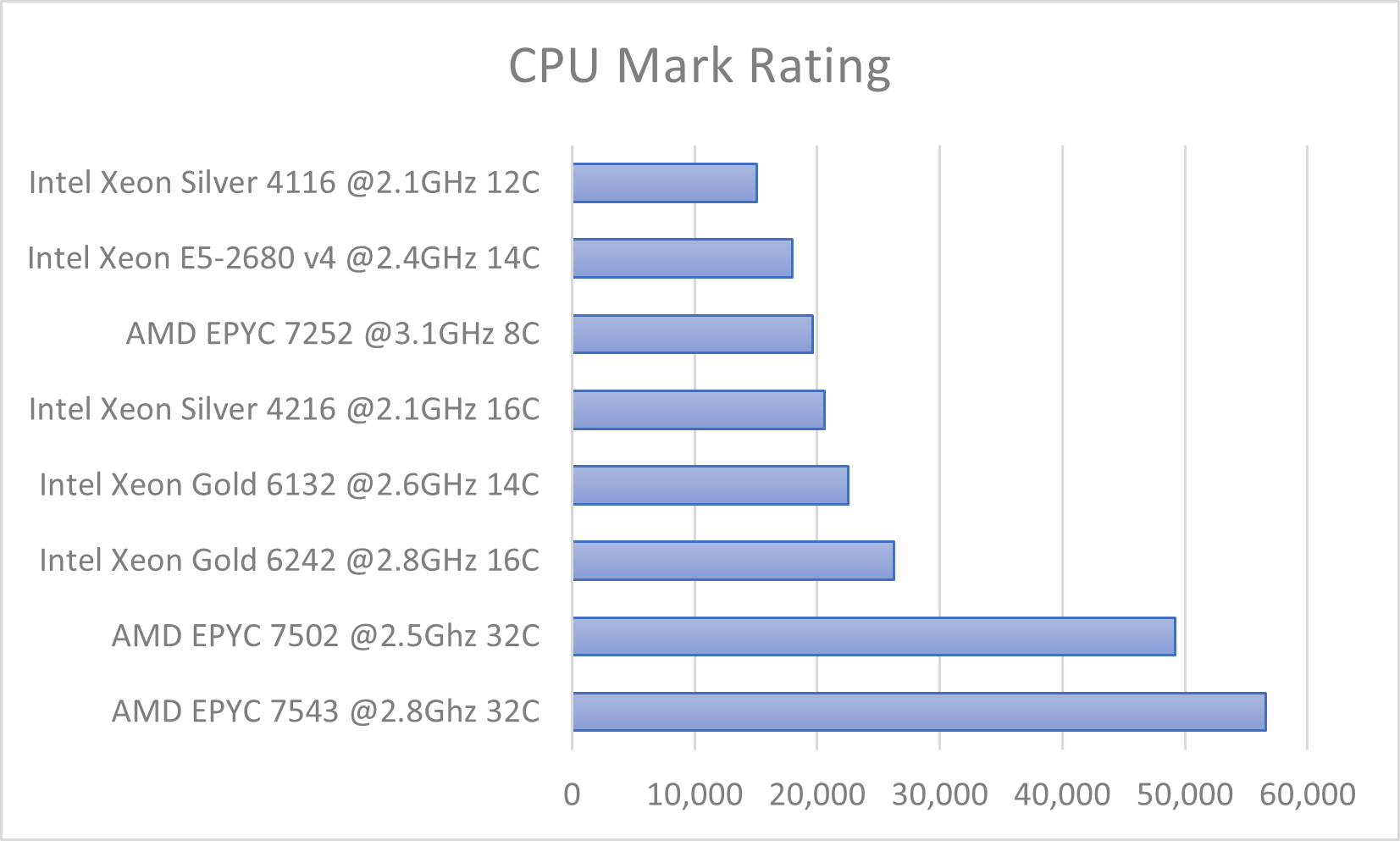
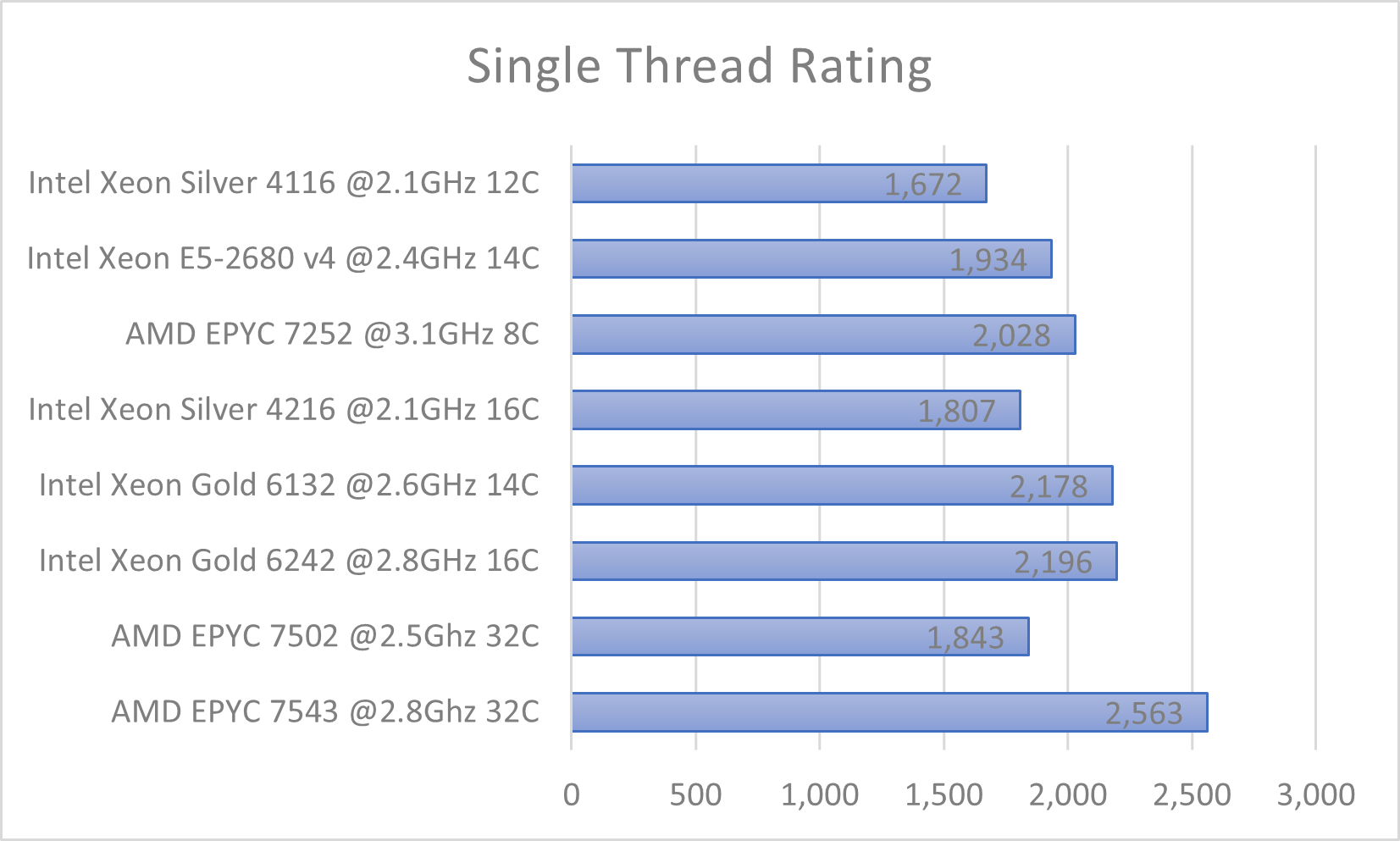
The following graphs show the relative performance of the different CPU types available within the cluster, scored using CPU PassMark (as of March 2023). Higher numbers are better.
Details of which nodes use which CPUs are below:
CPU |
Node name begins with |
|---|---|
Intel Xeon Silver 4116 @2.1GHz 12C |
n19-32-* |
Intel Xeon E5-2680 v4 @2.4GHz 14C |
n17-28-* |
AMD EPYC 7252 @3.1GHz 8C |
n21-16-* |
Intel Xeon Silver 4216 @2.1GHz 16C |
n19-24-* |
Intel Xeon Gold 6132 @2.6GHz 14C |
n19-28-* |
Intel Xeon Gold 6242 @2.8GHz 16C |
n19-64-* |
AMD EPYC 7502 @2.5Ghz 32C |
n21-64-* |
AMD EPYC 7543 @2.8Ghz 32C |
n23-64-* |
Tip
The System Overview page gives a full breakdown of the nodes and their various specifications.
Network throughput
The cluster’s compute and storage nodes are linked together using network switches that support 100-gigabit speeds (over 1,000 times faster than the UK’s average broadband speed of 100-megabits), with dual-bonding employed across the storage nodes. Interlinks between the switches run at 800 Gbps (gigabits per second). All together, this allows for a maximum data transfer rate of around 15 to 20 GB/s (gigaBYTEs per second), although this is generally only seen when running highly-parallel tasks.